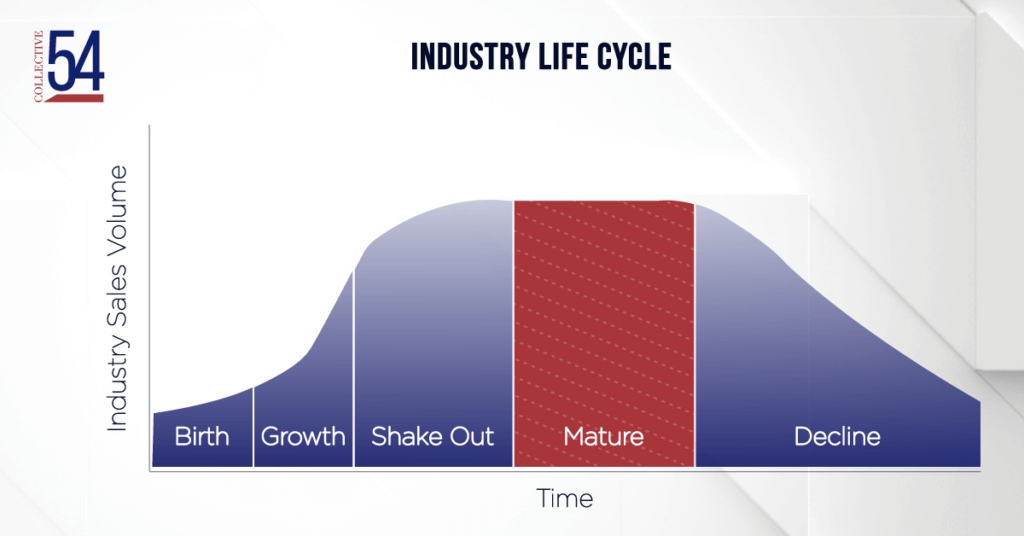
How Professional Service Firms Win in a Mature Industry
Many professional service firms compete in mature industries. This overview of the mature industry environment, its challenges, and strategies for success can provide a starting point for founders to find their way.